-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
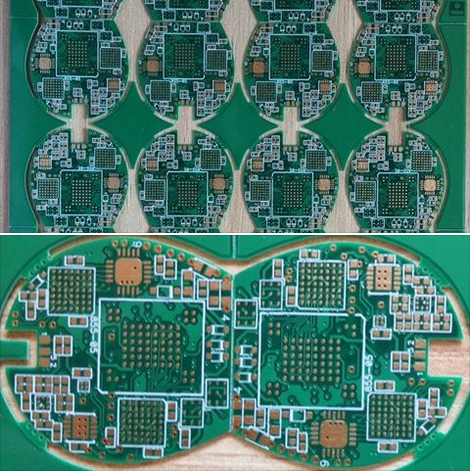
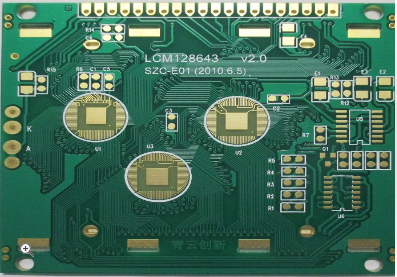
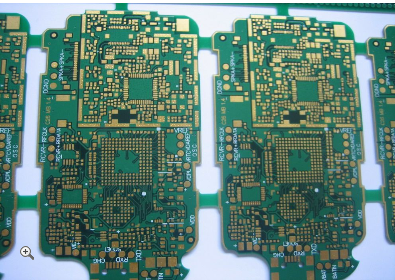
High Precision Plating Half Holes PCB Solutions For Complex Circuit Board Applications And Miniaturization
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics, the relentless drive towards greater functionality in smaller form factors presents formidable challenges for printed circuit board (PCB) design and manufacturing. As devices shrink from bulky industrial equipment to wearable gadgets and sophisticated medical implants, conventional PCB interconnection methods often reach their physical and electrical limits. It is within this context of complexity and miniaturization that High Precision Plating Half Holes (also known as castellated holes or plated half-holes) emerge as a critical and elegant solution. This advanced PCB technology is not merely an incremental improvement but a foundational enabler for modern electronic assembly, allowing for robust, space-efficient, and reliable board-to-board or module-to-board connections. By transforming the edge of a PCB into a conductive, solderable interface, it eliminates the need for traditional connectors or complex wiring in many applications, paving the way for more compact, cost-effective, and high-performance electronic systems. This article delves into the intricacies of High Precision Plating Half Holes, exploring their role in tackling the demands of complex circuit board applications and the ongoing trend of miniaturization.
The Technical Foundation and Manufacturing Process
The creation of High Precision Plating Half Holes is a testament to advanced PCB fabrication capabilities. Fundamentally, these are plated through-holes (PTHs) that are drilled at the very edge of a PCB substrate. After the standard drilling and copper plating process that creates a conductive barrel, the board is precisely routed or scored, slicing the plated through-hole exactly in half along its diameter. What remains is a row of semi-circular, metallized pads lining the board's edge.
The precision in this process cannot be overstated. The routing must be exceptionally accurate to ensure a clean cut through the center of the hole without damaging the fragile copper plating or delaminating the board material. Any deviation can lead to irregular plating, poor solderability, or mechanical weakness. Following the routing, the half-holes undergo meticulous plating, often involving multiple layers such as copper, nickel, and a final finish like gold (ENIG or ENEPIG) or immersion tin. This final plating ensures excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and a reliable electrical connection when the castellated module is soldered onto a motherboards. The entire process demands stringent process control, high-quality materials, and sophisticated equipment to achieve the consistency required for automated assembly.
Enabling Miniaturization and High-Density Design
One of the most significant advantages of half-hole technology is its direct contribution to product miniaturization. In traditional designs, connecting a smaller PCB module (like a Wi-Fi or Bluetooth module) to a main board typically requires a dedicated connector or a header. These components consume valuable vertical height (Z-axis space) and substantial board real estate (X-Y axis space). Castellated holes eliminate this intermediary entirely.
The module itself becomes its own connector. By soldering the half-holes directly onto corresponding pads on the target PCB, the two boards can be mounted flush or in very close proximity. This approach dramatically reduces the overall stack height, which is paramount in ultra-thin devices like smartphones, tablets, and hearing aids. Furthermore, it frees up surface area on both boards that would have been occupied by connector footprints, allowing designers to pack more components or routing into the same space. This leads to higher functional density, a key metric in the advancement of portable and implantable electronics where every cubic millimeter is precious.
Enhancing Reliability in Complex Applications
Beyond saving space, High Precision Plating Half Holes offer superior mechanical and electrical reliability compared to many alternative connection methods, which is crucial for complex and demanding applications. In automotive, aerospace, and industrial electronics, connections must withstand vibration, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. A properly soldered castellated joint forms a robust mechanical bond along the entire semi-circular surface, providing excellent resistance to shock and vibration.
Electrically, the connection is direct and short, minimizing parasitic inductance and capacitance that can degrade high-frequency signal integrity. This is vital for RF modules, high-speed communication boards, and sensitive analog circuits. The plated metallization ensures a gas-tight connection, preventing oxidation and maintaining long-term conductivity. For mission-critical applications, this reliability translates to enhanced product lifespan and reduced failure rates. The technology also simplifies the assembly process by enabling direct reflow soldering alongside other surface-mount components, reducing manual labor and potential points of failure introduced by press-fit connectors or hand-soldered wires.
Driving Innovation in Modular and System-in-Package Designs
The versatility of castellated hole technology is catalyzing innovation in system architecture, particularly in modular design and System-in-Package (SiP) approaches. Designers can now create standardized, pre-certified functional blocks—such as power management units, sensor hubs, or radio cores—on small daughter boards with castellated edges. These modules can be mass-produced and tested independently, then seamlessly integrated as building blocks into a larger system. This modularity accelerates development cycles, simplifies testing and debugging, and allows for easy upgrades or customization.
In advanced SiP and multi-board systems, half-holes facilitate the creation of compact, three-dimensional stacking configurations. Multiple PCB layers or sub-assemblies can be interconnected vertically using their castellated edges, creating complex, high-performance systems in an extremely compact footprint. This is increasingly important for Internet of Things (IoT) edge devices, where a single package may need to contain processing, sensing, communication, and power functionalities. High Precision Plating Half Holes provide the reliable, high-density interconnects needed to make these sophisticated integrations possible and manufacturable at scale.
In conclusion, High Precision Plating Half Holes represent a pivotal solution at the intersection of PCB manufacturing and advanced electronic design. By offering a unique combination of space savings, mechanical robustness, electrical performance, and design flexibility, they directly address the core challenges of complexity and miniaturization. As electronic devices continue to evolve towards greater intelligence in smaller packages, the demand for such precision interconnection technologies will only intensify. From enabling the next generation of wearables and medical devices to ensuring the reliability of automotive control systems, castellated hole technology stands as a critical enabler, allowing engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible in the ever-shrinking world of electronics.
REPORT